
Registration
Parental leave and parental allowance
Communication module
Area navigation
Starting a family
Starting a family
Parental leave & parental allowance

Parental leave
When a child is born, employees have a legal entitlement to a total of 36 months of parental leave, either as unpaid time off from work or in the form of a reduction in working hours. This entitlement applies to mothers and fathers who live with their child in the same household and raise and care for it themselves. Both parents can take parental leave at the same time or separately.
Parental leave can be divided into three periods by each parent. A maximum of 24 months of the total three-year parental leave can also be taken at a later date (until the child reaches the age of eight) without the employer's consent. For example, it is possible to provide intensive support for the child when they start school and during their first years at school and thus be there for them in important phases of their lives.
Between the birth and the third birthday of the child, the desired parental leave must be notified to the employer in writing seven weeks before the start of the leave. For this age period, the employee must make a binding commitment as to the periods of parental leave to be taken within two years. This commitment serves to provide the employer with planning security and is binding.
Between the child's third and eighth birthday, the notice period for parental leave is 13 weeks. Parental leave does not require the employer's consent. However, the employer must certify the parental leave upon request.
There is protection against dismissal during the entire period of parental leave. This applies from the time the notice is given, but no earlier than eight weeks before the start of parental leave.
Parental leave can also be reduced to part-time work of between 15 and 30 hours. The same notice periods of seven or 13 weeks apply when applying for part-time work. The employer must make the decision on the part-time application in writing within four weeks (eight weeks for part-time work after the third birthday). A rejection in companies with more than 15 employees is only permitted for urgent operational reasons and must be based on difficulties caused by the requested part-time employment. During part-time parental leave, a reduction in working hours may be requested twice.
A detailed description of all parental leave regulations in our factsheet "Information on parental leave".
Parental allowance + parental allowance plus
Parental allowance gives mothers and fathers the opportunity to interrupt or reduce their employment in order to concentrate intensively on caring for the new addition to the family. The state parental allowance compensates for the loss of income. The amount is usually calculated on the basis of the average gross income (minus lump sums for taxes and social security contributions) of the last 12 months before the birth of the child. Parental allowance amounts to a minimum of 300 euros and a maximum of 1,800 euros per month. The replacement rate is between 65% and 100% of the previous income. The lower the income, the higher the replacement rate.
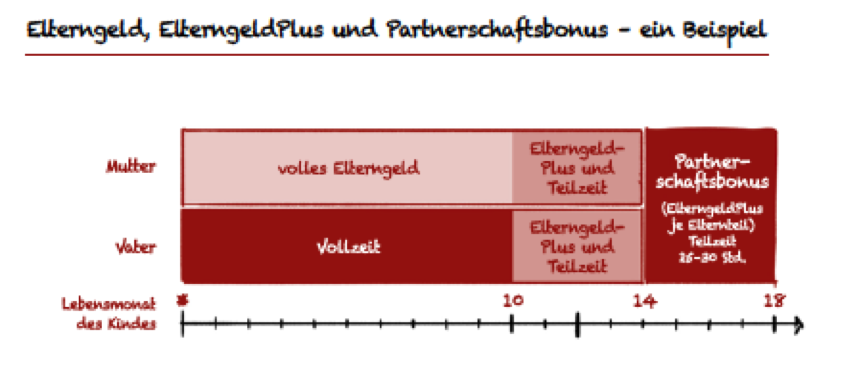
An important aim of parental allowance is to motivate fathers to take on more family responsibility and care duties. The classic parental allowance is paid to both parents for a maximum of 14 months of the child's life, and both parents are free to divide the period between them. For example, they can receive parental allowance together for seven months or one parent can receive it for the first seven months and the other parent for the second seven months. One parent can claim a maximum of twelve months alone, with a further two months reserved as an option for the partner. This means that if one parent does not take any time off to care for the child, they are only entitled to a total of 12 months' parental allowance. However, single parents are also entitled to 14 months of parental allowance alone.
Parental Allowance Plus is intended to offer greater flexibility and partnership in the division of childcare time between the parents and attractive options for a faster return to work. Parents whose children are born on or after July 1, 2015 can choose between the 'classic' parental allowance and Parental Allowance Plus or combine these two options.
Parental Allowance Plus makes it more attractive to work part-time while receiving parental allowance. While the "classic" parental allowance ends after 14 months of the child's life at the latest, Parental Allowance Plus can be extended by working part-time. In financial terms, one month of parental allowance becomes two months of Parental Allowance Plus. This means that the amount of parental allowance paid out each month is halved.
With the newly introduced partnership bonus, both parents can each gain four additional months of parental allowance plus. The prerequisite for this is that the father and mother share the care of the child and work between 25 and 30 hours per week for four months at the same time.
Part-time work while receiving parental allowance affects the amount of parental allowance. Parental allowance only ever replaces income that is actually lost. Additional earnings are therefore deducted from the average earnings before the birth, and the replacement rate of up to 67% is applied to the difference (= lost income).
Parental allowance is applied for at the respective local authority. As it is only granted retroactively three months after the application is submitted, the application should be submitted in good time after the birth of the child. The processing time, which can take several months in some municipalities and during which parents have to bridge the income gap, should not be neglected.
A detailed description of all the important aspects of parental allowance can be found in the enclosed factsheet "Information on parental allowance", which you can print out and hand out to expectant parents.
Opportunities and design options for employers
How long parental leave is taken and how parents divide the parental allowance months and career breaks between them is initially a decision between the two partners. However, the employer can have an important influence on the decision through information and communication.
The legal framework, including deadlines to be met and the recommendation that applications and approvals or rejections be made in writing, set a minimum standard for parental leave and return. In addition, there are no limits to the flexible handling of reductions and increases in working hours. The condition is that the parties involved are in agreement.
When finding joint solutions, it is important to communicate your ideas and wishes for parental leave at an early stage. Is a complete break planned or just a reduction in working hours? How can contact be maintained during parental leave? What return-to-work models are conceivable? Can parental leave be used for further training? How are substitute solutions arranged?
The new Parental Allowance Plus offers advantages for companies, as it helps mothers and fathers to return to work more quickly after the birth of a child. The partnership bonus makes it interesting for both parents to return to work full-time in good time.
Suggestions and measures on what companies and parents can do during parental leave to maintain contact and use the time profitably can be found in the document "Ideas and regulations for companies on the subject of parental leave".



